Acute Malnutrition Ncbi
1993 Aug 42705. So far in Sub-Saharan Africa several primary studies have been conducted on recovery rate and determinants of recovery from SAM in under-five children.

Marasmus Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf
In many malnourished patients there is an associated disease-related inflammation resulting in a complex interplay between the two.
Acute malnutrition ncbi. Disease-related malnutrition arises due to reduced dietary intake malabsorption increased nutrient losses or altered metabolic demands. Despite this malnutrition remains a major cause of illness and death among children worldwide particularly in low- and medium-income countries. Fluid management of children with severe acute malnutrition 46 7.
A cluster randomized controlled trial. Background Severe acute malnutrition is defined by. Severe acute malnutrition is a major cause of death in children under 5 and its.
1 Food deprivation lack of maternal education inappropriate feeding and infections could be the major causes for the latter type of malnutrition2 Malnutrition is a leading killer in children under five years3 World Health Organization WHO defines Severe Acute Malnutrition SAM as a very low weight for height by visible severe wasting. National Library of Medicine. The two principal forms of SAM are.
The primary objective of this study is to. Acute malnutrition and high childhood mortality related to diarrhea. Undernutrition and severe acute malnutrition SAMare global pediatric public health problems 1 2Owing to acute undernutrition globally 52 million under-5 children experience wasting approximately 77 and 17 million under-5 children experience SAM Children with weight-for-height below three standard deviations mid-upper arm.
Global acute malnutrition was found in 133 of overall screened children while 49 had severe acute malnutrition SAM and 84 had moderate acute malnutrition. Hussain I Habib A Ariff S Khan GN Rizvi A Channar S et al. CMAM is evidently effective in resolving SAM but little evidence exists on the remaining risk of SAM relapse for children discharged as cured from the OTP.
Advances in our understanding of the treatment of severe acute malnutrition SAM in a resource-limited environment are needed to improve outcome. Introduction Moderate to severe acute malnutrition SAMMAM and severe anaemia are important and associated co-morbidities in children aged less than five years. Severe acute malnutrition SAM is caused by a significant imbalance between nutritional intake and individual needs.
Background Globally Severe Acute Malnutrition SAM has been reduced by only 11 over the past 20 years and continues to be a significant cause of morbidity and mortality. PubMedNCBI Google Scholar 9. Childhood acute malnutrition is a global health problem and lifethreatening condition.
Severe acute malnutrition is the most extreme and visible form of undernutrition plagued by chronic poverty household food insecurity lack of education. None of the therapeutic foods used to treat. Degrees of malnutrition are associated with increased risk of all-cause mortality and increased risk of.
Lessons from the 1991 Kurdish refugee crisis JAMA. Independently these two morbidities are responsible for high risk of in-hospital and post-discharge deaths and hospital readmissions. Management of HIV-infected children with severe acute malnutrition 55 8.
Always feeling cold. We find that while combinedsimplified protocols for outpatient management of uncomplicated cases of acute malnutrition are being used in emergency situations in all four countries there is widespread confusion about protocol terminology and content stemming from a lack of coherence at the global level. It is most often caused by both quantitative number of kilocaloriesday and qualitative vitamins and minerals etc deficiencies.
- The aim of my research is to asses s availability of health. Wide-ranging changes in physiological function occur in malnourished patients leading to increased rates of. The high rates of malnutrition and mortality related to diarrhea in infants and younger children of Kurdish refugees took place rapidly despite prompt relief efforts and a previously healthy population.
The explanation for this association may be that the management of acute malnutrition is similar regardless of whether stunting is present although of course the most stunted children will have the highest risk of failure to respond to therapy and requiring a longer hospital stay. An inability to concentrate. Ready-to-use therapeutic foods RUTFs made from local products and with reduced milk content lower costs and may be effective in older children.
Acute malnutrition is caused by complex and intertwined factors with large time and geographic variability Marshak Young Bontrager Boyd 2017Globally acute malnutrition still affects 505 million children under 5 years old and those who are moderately or severely. A lack of appetite or interest in food or drink. Effectiveness of management of severe acute malnutrition SAM through community health workers as compared to a traditional facility-based model.
Each year approximately 59 million children around the world die before their fifth birthday You and others 2015. One of the problems of diagnosing malnutrition is the lack of a unified definition and of standard methods for screening and diagnosis. One of the indigenous and marginalized community of Nepal SatarSanthal has often.
Children over 6 months of age. No distinction is made between the clinical conditions of kwashiorkor or severe wasting because their treatment is similar. Some signs and symptoms of malnutrition include.
Malnutrition results from a mismatch of nutritional requirements with intake. The leading killers are prematurity and pneumonia responsible for 178 percent and 155 percent of all deaths in this age group respectively Liu and others 2014 2016. One-fifth of the children under six months of age were acutely malnourished followed by children under two years at 185 based on weight-for-height z scores.
Severe acute malnutrition SAM among children in Nigeria is tackled through the outpatient therapeutic programme OTP of the Community-based Management of Acute Malnutrition CMAM programme. Marasmus and kwashiorkor are the most life-threatening forms of malnutrition. Treatment protocols enable effective treatment but only a minority of malnourished children have access to treatment.
Malnutrition is a common under-recognised and undertreated condition in hospital patients. Identifying and managing infants who are less than 6 months of age with severe. Therapeutic feeding approaches in the management of severe acute malnutrition in children who are 659 months of age 36 6.
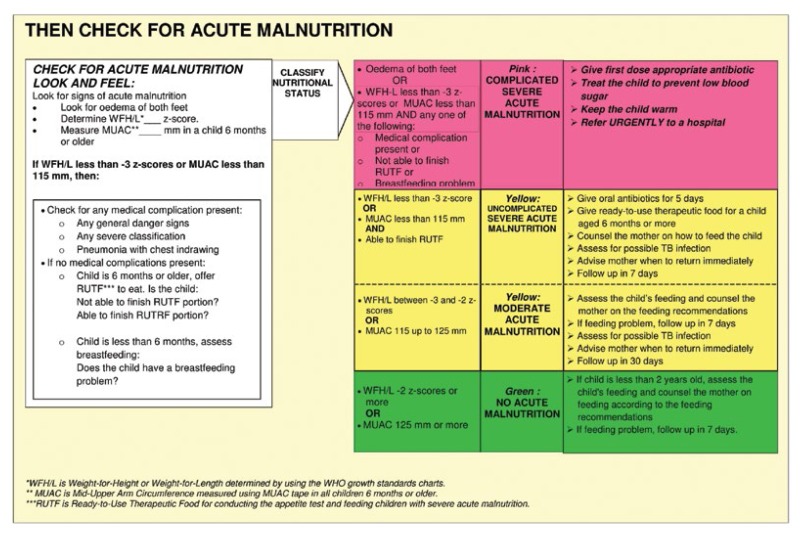
Severe acute malnutrition is defined in these guidelines as the presence of oedema of both feet or severe wasting weight-for-heightlength.

Figure 11 1 Conceptual Framework Of Determinants Of Undernutrition Reproductive Maternal Newborn And Child Health Ncbi Bookshelf
Management Of Severe And Moderate Acute Malnutrition In Children Reproductive Maternal Newborn And Child Health Ncbi Bookshelf

Fig 12 Strategies To Reduce The Cost Of Treatment For Severe Acute Malnutrition Who Guideline On The Dairy Protein Content In Ready To Use Therapeutic Foods For Treatment Of Uncomplicated Severe Acute Malnutrition

Fig 1 Imci Flow Chart On Anthropometric Assessment And Classification Of Nutritional Status Guideline Assessing And Managing Children At Primary Health Care Facilities To Prevent Overweight And Obesity In The Context

Interventions For Malnutrition In Older Adults A Review Of Clinical Effectiveness Ncbi Bookshelf
Evidence And Recommendations Guideline Assessing And Managing Children At Primary Health Care Facilities To Prevent Overweight And Obesity In The Context Of The Double Burden Of Malnutrition Ncbi Bookshelf

Fig 11 Rutf Macro Cost Breakdown Who Guideline On The Dairy Protein Content In Ready To Use Therapeutic Foods For Treatment Of Uncomplicated Severe Acute Malnutrition Ncbi Bookshelf

Figure 11 2 World Health Organization S 10 Step Plan For The Management Of Severe Acute Malnutrition Reproductive Maternal Newborn And Child Health Ncbi Bookshelf
Management Of Severe And Moderate Acute Malnutrition In Children Reproductive Maternal Newborn And Child Health Ncbi Bookshelf
0 Response to "Acute Malnutrition Ncbi"
Post a Comment